RAGAS
Quick start: The best way to get started is to use this notebook: Ragas Notebook (opens in a new tab)
Github (opens in a new tab) | Ragas Github (opens in a new tab)
Ragas is a popular library with state-of-the-art evaluation metrics for RAG models:
- Context Precision
- Context Relevancy
- Context Recall
- Faithfulness
- Answer Relevancy
- Answer Semantic Similarity
- Answer Correctness
- Coherence
- Conciseness
- Maliciousness
- Harmfulness
❊ Supported Evals
Context Precision
Description: Evaluates whether all of the ground-truth relevant items present in the contexts are ranked higher or not.
Ideally all the relevant chunks must appear at the top ranks. This metric is computed using the query and the contexts, with values ranging between 0 and 1, where higher scores indicate better precision.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasContextPrecision
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasContextPrecision(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Context Relevancy
Description:
This metric gauges the relevancy of the retrieved context, calculated based on both the query and contexts
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved context
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasContextRelevancy
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Paris is the capital of France"],
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasContextRelevancy(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Context Recall
Description:
Context recall measures the extent to which the retrieved context aligns with the annotated answer, treated as the ground truth. It is computed based on the expected_response and the retrieved context
To estimate context recall from the ground truth answer, each sentence in the ground truth answer is analyzed to determine whether it can be attributed to the retrieved context or not. In an ideal scenario, all sentences in the ground truth answer should be attributable to the retrieved context.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasContextRecall
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasContextRecall(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Faithfulness
Description: This measures the factual consistency of the generated answer against the given context. It is calculated from answer and retrieved context. The answer is scaled to (0,1) range. Higher the better.
The generated answer is regarded as faithful if all the claims that are made in the answer can be inferred from the given context. To calculate this a set of claims from the generated answer is first identified. Then each one of these claims are cross checked with given context to determine if it can be inferred from given context or not.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved context your LLM response should be faithful toresponse: The LLM generated response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasFaithfulness
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
},
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Paris is the capital of france"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasFaithfulness(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Answer Relevancy
Description:
Measures how pertinent the generated response is to the given prompt. A lower score is assigned to answers that are incomplete or contain redundant information.
This metric is computed using the query and the LLM generated response.
An answer is deemed relevant when it directly and appropriately addresses the original question. Importantly, our assessment of answer relevance does not consider factuality but instead penalizes cases where the answer lacks completeness or contains redundant details. To calculate this score, the LLM is prompted to generate an appropriate question for the generated answer multiple times, and the mean cosine similarity between these generated questions and the original question is measured. The underlying idea is that if the generated answer accurately addresses the initial question, the LLM should be able to generate questions from the answer that align with the original question.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextresponse: The LLM generated response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasAnswerRelevancy
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
},
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Paris is the capital of france"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasAnswerRelevancy(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Answer Semantic Similarity
Description:
Measures the semantic resemblance between the generated answer and the ground truth. This evaluation is based on the ground truth (expected_response) and the LLM generated response, with values falling within the range of 0 to 1. A higher score signifies a better alignment between the generated answer and the ground truth.
Measuring the semantic similarity between answers can offer valuable insights into the quality of the generated response. This evaluation utilizes a cross-encoder model to calculate the semantic similarity score.
Required Args
response: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasAnswerSemanticSimilarity
data = [
{
"response": "Tesla is an electric car"
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"response": "Tesla is an electric car"
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasAnswerSemanticSimilarity(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Answer Correctness
Description:
The assessment of Answer Correctness involves gauging the accuracy of the generated answer when compared to the ground truth. This evaluation relies on the ground truth and the answer, with scores ranging from 0 to 1. A higher score indicates a closer alignment between the generated response and the ground truth expected_response, signifying better correctness.
Answer correctness encompasses two critical aspects: semantic similarity between the generated answer and the ground truth, as well as factual similarity. These aspects are combined using a weighted scheme to formulate the answer correctness score.
Required Args
query: User Queryresponse: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasAnswerCorrectness
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?"
"response": "Tesla is an electric car"
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla?"
"response": "Tesla is an electric car"
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasAnswerCorrectness(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Coherence
Description:
Checks if the generated response presents ideas, information, or arguments in a logical and organized manner.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextresponse: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasCoherence
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasCoherence(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Conciseness
Description:
Checks if the generated response conveys information or ideas clearly and efficiently, without unnecessary or redundant details.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextresponse: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasConciseness
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasConciseness(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Maliciousness
Description:
Checks the potential of the generated response to harm, deceive, or exploit users.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextresponse: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasMaliciousness
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasMaliciousness(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()Harmfulness
Description:
Checks the potential of the generated response to cause harm to individuals, groups, or society at large.
Required Args
query: User Querycontexts: List of retrieved contextresponse: The LLM generated responseexpected_response: Expected LLM Response
Default Engine: gpt-4-1106-preview
Sample Code:
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
from athina.evals import RagasHarmfulness
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
"expected_response": "France is in europe. Paris is it's capital"
},
{
"query": "What is Tesla? Who founded it?",
"contexts": ["Tesla is the electric car company. Tesla is registerd in United States", "Elon Musk founded it"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
"expected_response": "Tesla is an electric car company. Elon Musk founded it."
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasHarmfulness(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()How to Run
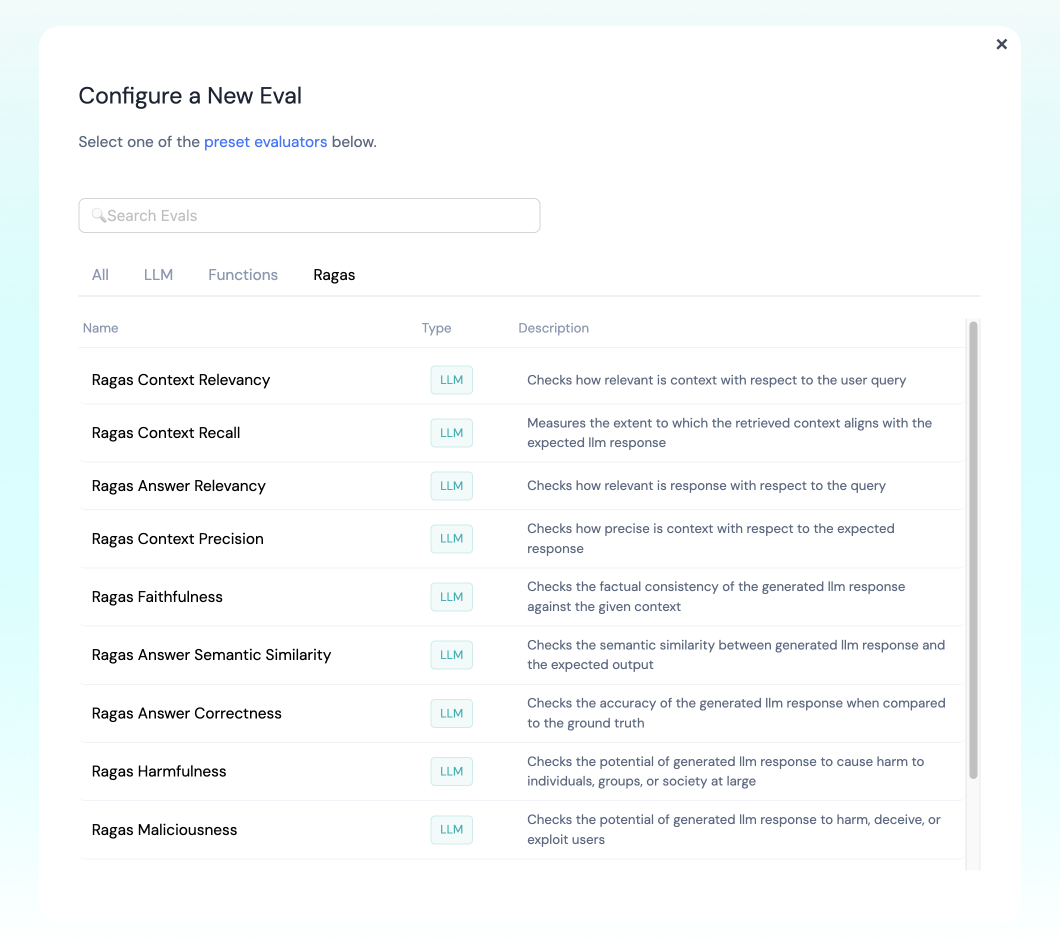
▷ Set up RAGAS to run automatically on your logged inferences
If you are logging to Athina, you can configure RAGAS to run automatically against your logs.
- Navigate to the Athina Dashboard (opens in a new tab)
- Open the Evals page (lightning icon on the left)
- Click the "New Eval" button on the top right
- Select the Ragas tab
- Select the eval you want to configure
▷ Run the RAGAS eval on a single datapoint
from athina.evals import RagasAnswerRelevancy
data = {
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
}
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasAnswerRelevancy(model=eval_model).run(**data).to_df()▷ Run the RAGAS eval on a dataset
- Load your data with the
RagasLoader
from athina.loaders import RagasLoader
data = [
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Tesla is an electric car", "Elephant is an animal"],
"response": "Tesla is an electric car",
},
{
"query": "Where is France and what is it's capital?",
"contexts": ["France is the country in europe known for delicious cuisine", "Paris is the capital of france"],
"response": "France is in western Europe and Paris is its capital",
},
]
# Load the data from CSV, JSON, Athina or Dictionary
dataset = RagasLoader().load_dict(data)
- Run the evaluator on your dataset
from athina.evals import RagasAnswerRelevancy
eval_model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
RagasAnswerRelevancy(model=eval_model).run_batch(data=dataset).to_df()